You want to use the “house for plants” with maximum efficiency – so that vegetable crops can bask under the sun for a long time, be well lit and reliably protected from the wind, and in response to care, they try their best to please us with a harvest of juicy fruits. You will get it if you will know the right placewhere to put your greenhouse in the garden!
Every second gardener in the process of improving gardening skills sooner or later comes to the idea of installing a greenhouse. It is understandable – with this useful acquisition, the season can start earlier, end later, and harvest more. Well, who would refuse such a seductive prospect in our difficult times? So the decision is made quickly and without hesitation, after which the question immediately arises: where to install the greenhouse in order to get the maximum benefit from it? You will find the answer in this article.
So, what factors should be considered when choosing a place for a greenhouse on the site.
Orientation to the cardinal points
The illumination of plantings in a greenhouse (and hence the growth rate and crop yield) depends on the location of the building itself relative to the cardinal points. When choosing a place and method of accommodation, three options are usually considered:
- from North to South,
- from East to West,
- at an angle.
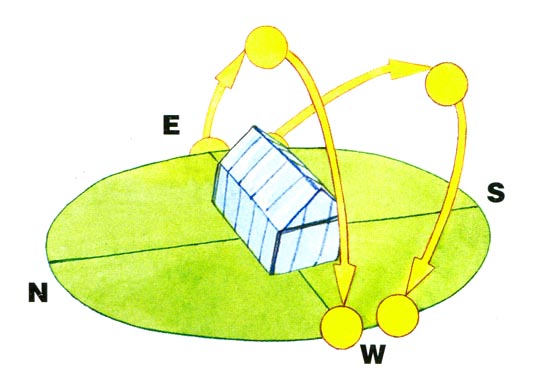
The location of the greenhouse along the north-south line makes it possible to give the plants more uniform illumination: in the first half of the day the sun warms the eastern side of the plantings, and in the afternoon it moves to the western. The plants also get a portion of sunlight from above and from the southern end of the greenhouse. It would seem that this is an ideal option, but it must be taken into account that most of the day the rays go tangentially (that is, their efficiency is lower), and the northern end receives almost no light. This placement of the greenhouse is recommended for southern latitudes, where solar radiation is stronger and perfectly warms the plants even with a “sliding” stream.
In the northern regions, the orientation of the greenhouse from east to west is considered optimal. With this placement of heat and light, plants get more – they can catch the sun’s rays from dawn to dusk. True, at the same time, plantings in the southern part of the greenhouse, which are better illuminated, occupy a more advantageous position. Having chosen this location, plant undersized crops on the south side so that they do not block all other plants from the sun.
Most often, it is impossible to place a greenhouse strictly along the north-south or west-east lines, because. there are already other buildings on the territory with which it needs to be “linked”. In this case, you can try the “middle” option – at an angle of 45 ° relative to the axes. It may turn out to be the most beneficial, since it combines the advantages of both schemes and is suitable for most climatic zones.
Note. If you plan to put a greenhouse near the house, then choose a place on the south side – in this case, the plants will receive maximum light and heat, because. the sun will illuminate them throughout the day, and the walls of the house will cover them from the piercing north wind. A good option would be the location also on the southeast or southwest side.
When working in a small area with lots of buildings and tall trees, if you can’t find open space, position your greenhouse so that the sun hits it in the early afternoon when it’s more active.
How to take into account the wind rose when locating your greenhouse on the site
We recommend that you pay special attention to the prevailing winds in your area when placing your greenhouse on the site. You should protect the “plant house” and its inhabitants from drafts and strong gusts of wind, which can harm not only the plants, but also the greenhouse itself.
Before installing the greenhouse, study the wind rose and, other things being equal, choose the quietest place on the site. Of course, it is not so easy to find a windproof and at the same time the best illuminated area – of these two characteristics, illumination will still be primary. But protection from the wind can be provided on your own – for example, plant a hedge on the north side of the greenhouse or build a low decorative fence that will not cover the sun, but will break the air currents.
Note. A hedge or fence should be placed at a distance of about 7 m from the greenhouse, and the height of the protective structures should be no more than 2 m with a greenhouse height of 2.5 m.
Where to place the greenhouse given the relief of the site
Before starting work on installing a greenhouse, it is necessary to study the landscape features of the site and determine the height of the groundwater. The greenhouse should be placed on a flat area where groundwater occurs no higher than 1.5 m from the ground level. If you do not take this recommendation into account, then instead of a rich harvest of vegetables, you will get a “headache” in the form of constant flooding of the greenhouse, rotting of plantings and damage to structural elements from excessive moisture. There is also a high risk of developing fungal diseases and freezing of plants, the appearance of mold and moss inside the building.
To avoid such troubles, it is worthwhile to carefully study the area where you plan to put a greenhouse. You should mark the boundaries of the future building with the help of pegs and observe how the landscape behaves under different weather conditions: does the soil erode, do puddles remain after the rains.
If it turns out that the location of the future greenhouse is regularly heated, and it is not possible to move it, then it is necessary to lay the foundation, which will ensure the stability of the building. Additionally, it is worth organizing drainage ditches to drain excess water.
If the site is not yet occupied by other buildings and there are different placement options, try to find a flat horizontal platform for the greenhouse without elevation changes. Ideally, if it is on a slight elevation, on dry and solid ground.
Soil quality
The quality of the soil is important for both the stability of the greenhouse and the high yield of the crops growing in it, so you should not neglect this parameter. Try to determine the mechanical composition of the soil in the area allocated for the greenhouse, and, based on the result, take further steps.
- The best option in terms of density and fertility would be loam – on such soil a greenhouse can be placed even without building a foundation, and the structure of the soil is suitable for most garden crops.
- Sandy or swampy peat soil has a low density, is easily eroded and is not able to hold any buildings. When installing a greenhouse on such soil, over time, subsidence can occur, the structure is skewed, cracks form in the covering material. The addition of fertile land will help improve the structure of the soil, and the foundation will provide the frame with the necessary stability.
- The worst option is dense clay soil. It does not let water through, slowly warms up, plants in such soil feel a lack of nutrition. The situation can be corrected as follows: dig a pit along the perimeter of the future greenhouse, arrange a gravel “cushion” at the bottom, then fill it with sand and pour a layer of fertile soil on top.
Distance from your house and other buildings
Many gardeners make the mistake of installing a greenhouse in the farthest corner of the site. Thus, of course, it is possible to hide the greenhouse from prying eyes, while maintaining the concept of landscape design, however, when maintaining the greenhouse, you have to sacrifice convenience. In addition, connection to communications (water and electricity) in this case requires more time and investment.
It is worthwhile to carefully approach the calculation of the distance from the greenhouse to other structures on the site.
According to the regulations, the minimum distance to the border of neighboring land ownership should be at least 1 m, however, experts recommend leaving more space before the fence to avoid snow drifts in winter and provide a convenient approach for cleaning the greenhouse. For the same reasons, indents from the house, barn and other buildings leave about 2-3 m.
A competent approach to the location of the greenhouse will allow you to use it to the maximum benefit and collect crops that your neighbors will envy. Such a course of events can have only one “minus”: over time, you will want more – greenhouses, hotbeds and beds!
